
Types of Wireless Networks Explained
Wireless networks vary in type and application, including Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) for local connectivity, Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) for cellular communication over[…]
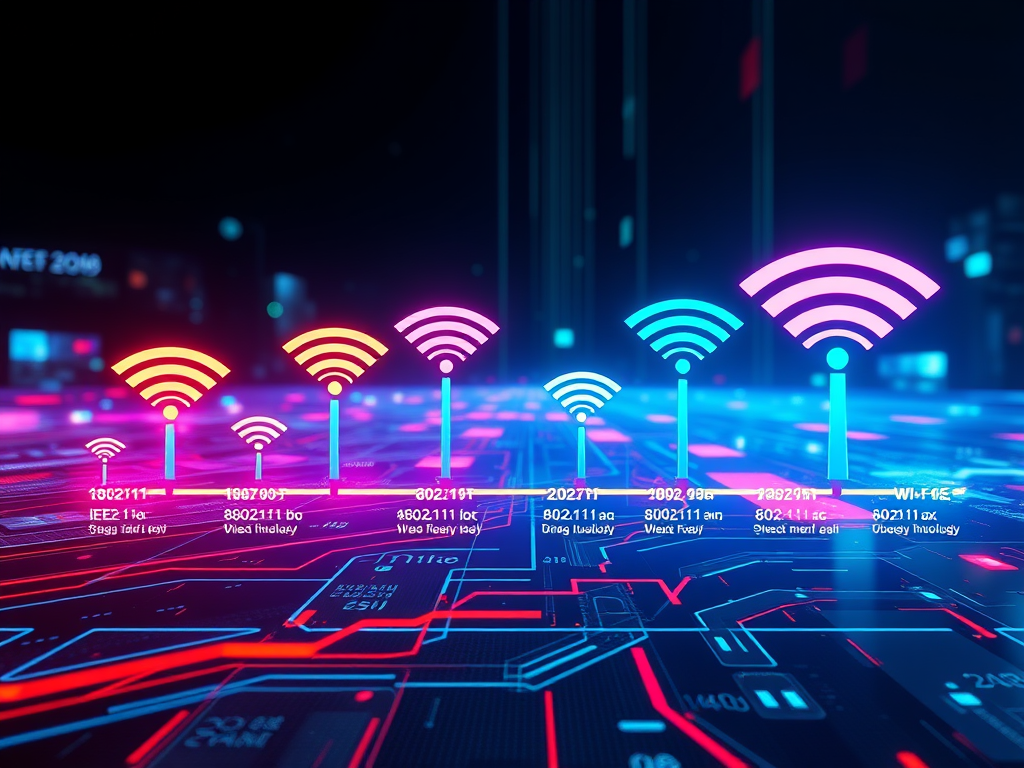

The Evolution of Wi-Fi Technology Since 1997
Wi-Fi technology has evolved significantly since the 1997 IEEE 802.11 standard, initially enabling 2 Mbps wireless data transfer. Key developments include 802.11b (1999) at 11[…]

What is a wireless network?
A wireless network allows devices to connect and communicate without physical cables, using radio frequency signals. It facilitates resource sharing and internet access in various[…]

What is the data transfer speed of Devices That Are Connected to Bluetooth?
Bluetooth data transfer speeds are influenced by the version used. Bluetooth 4.0 supports up to 25 Mbps, while 4.1 offers similar speeds with enhancements. Bluetooth[…]
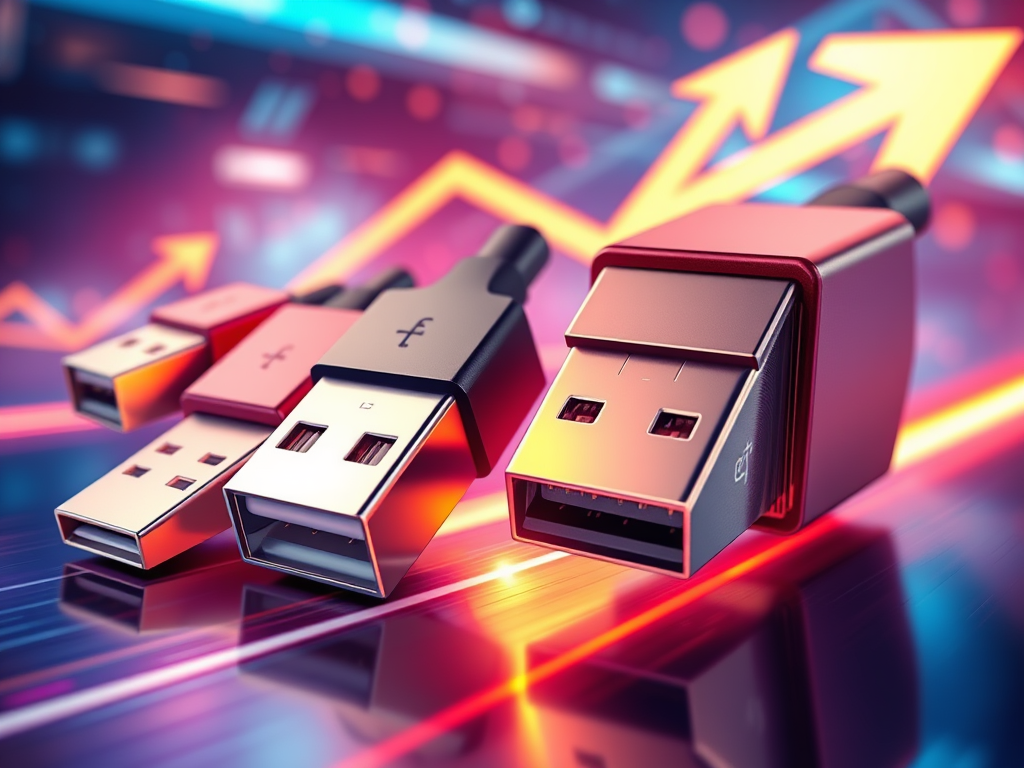

Understanding USB Data Transfer Speeds
USB technology has evolved through various standards, enhancing data transfer speeds significantly. These include USB 1.1 (1.5-12 Mbps), USB 2.0 (up to 480 Mbps), USB[…]

The WI-FI uses standard specifications
Wi-Fi technology relies on standardized specifications developed by IEEE under the 802.11 family, ensuring device compatibility, security, and performance. Key aspects include various standards like[…]
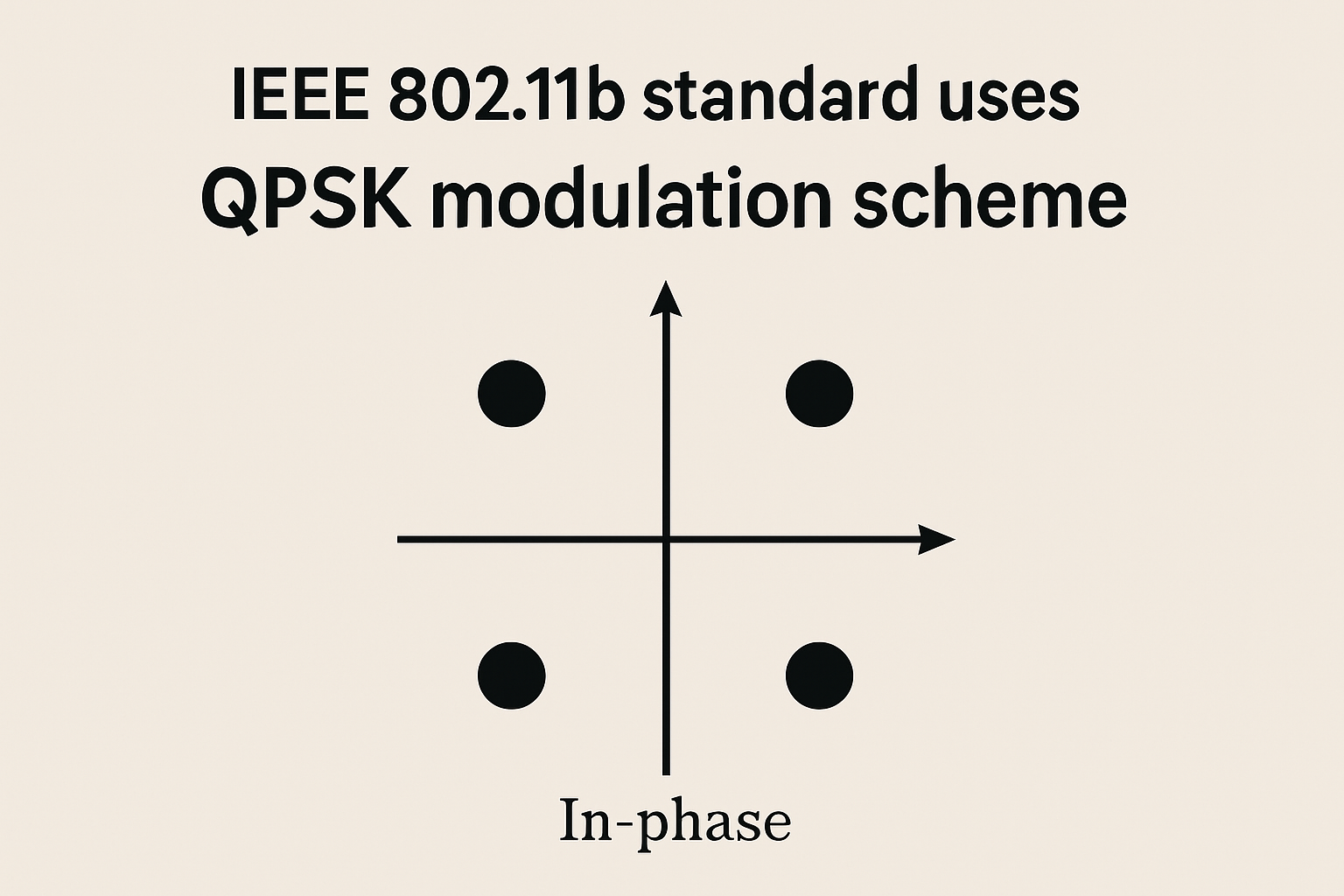
The Role of Key Modulation Techniques in IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11b, part of the WLAN standards, utilizes key modulation techniques like Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Complementary Code Keying (CCK). DSSS enhances interference[…]
What is ID when the wireless MANs?
In the context of Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs), the term “” typically refers to a unique identifier assigned to various network components or entities.[…]
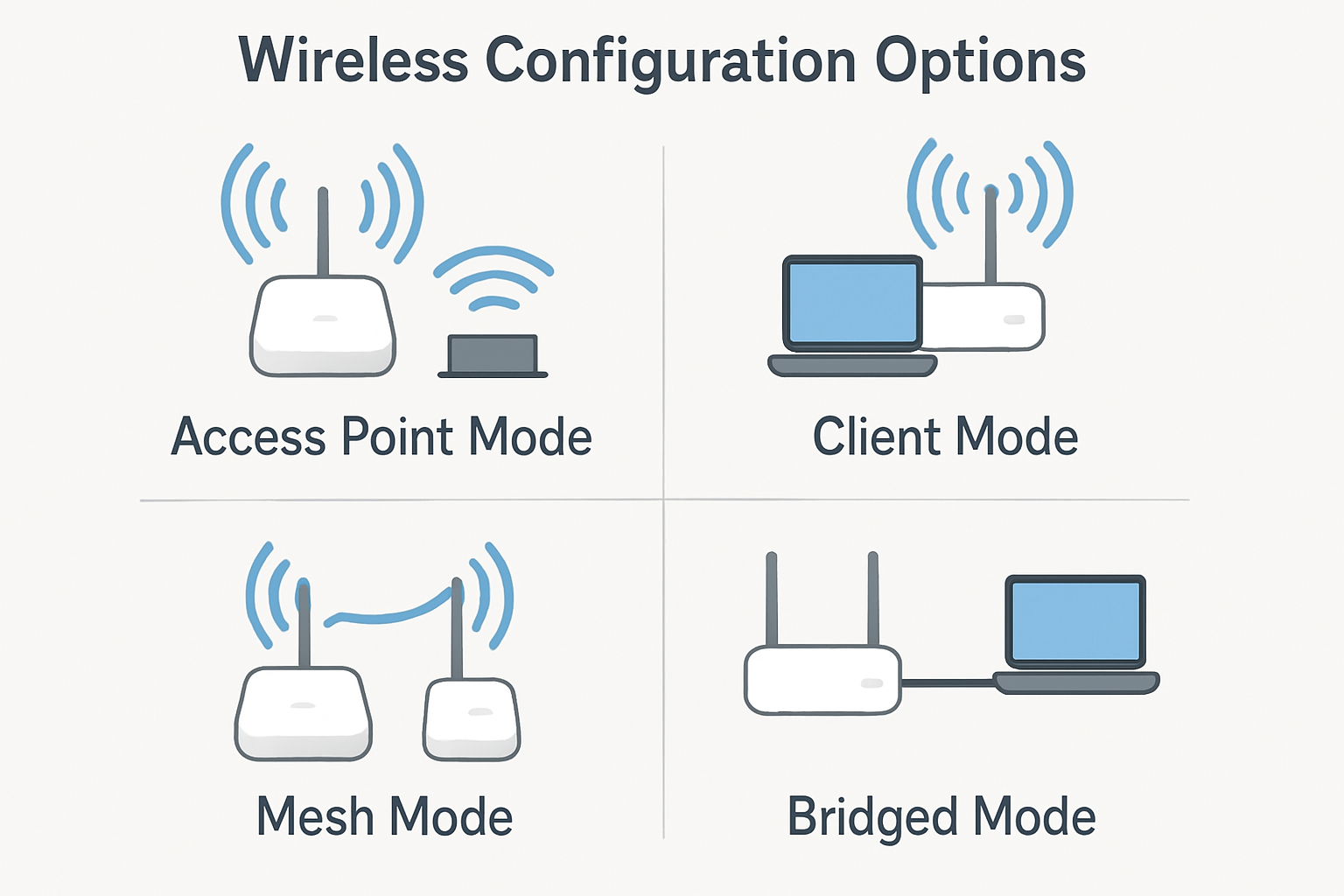
Maximize Wireless Network Configurations
The configuration of wireless stations, including access points and clients, can vary significantly based on several factors such as hardware capabilities, network requirements, security policies,[…]
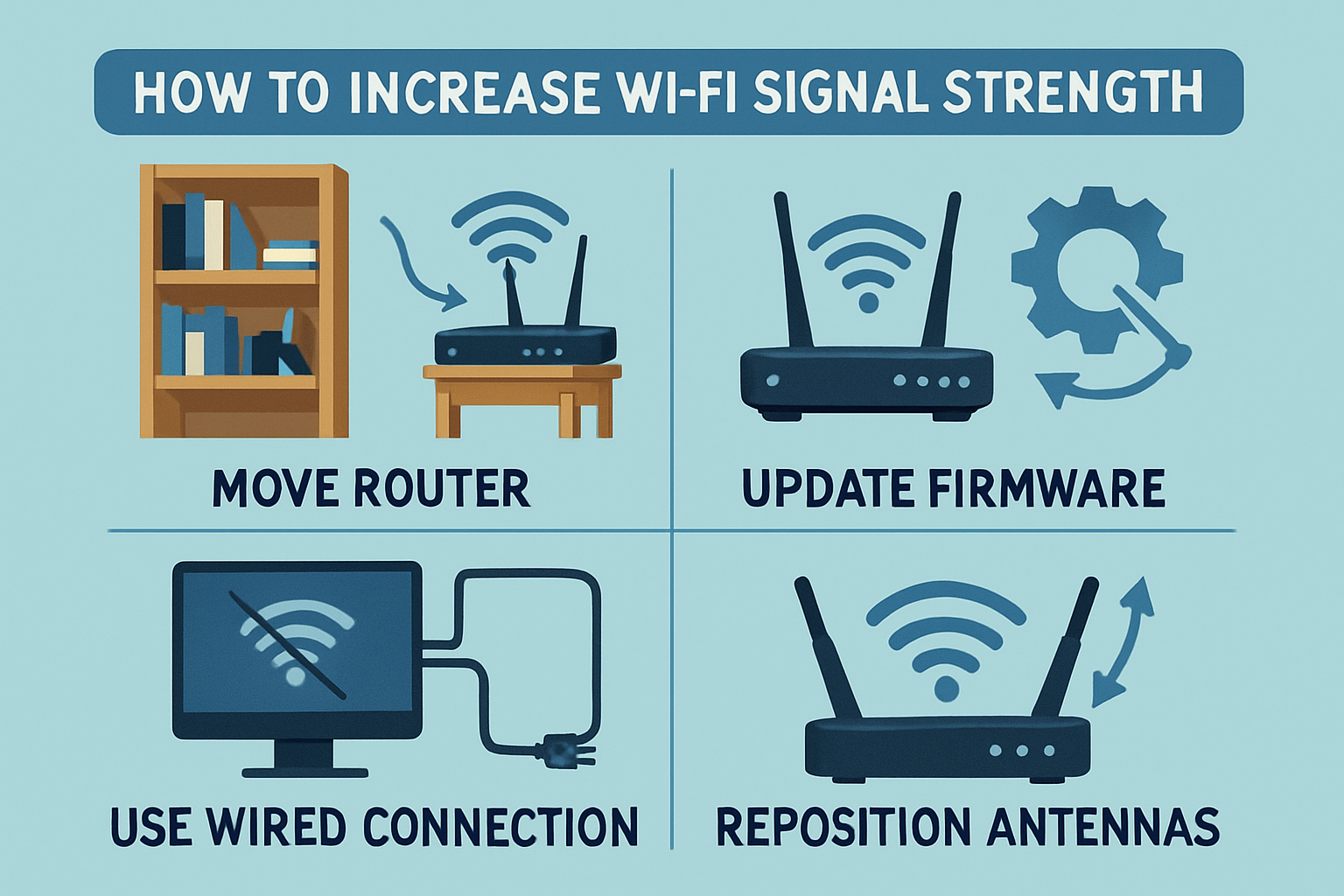
How can I increase my Wi-Fi signal strength?
1. Optimal Router Placement Position your router in a central location within your residence or office, elevated from the ground, and free from obstructions such[…]
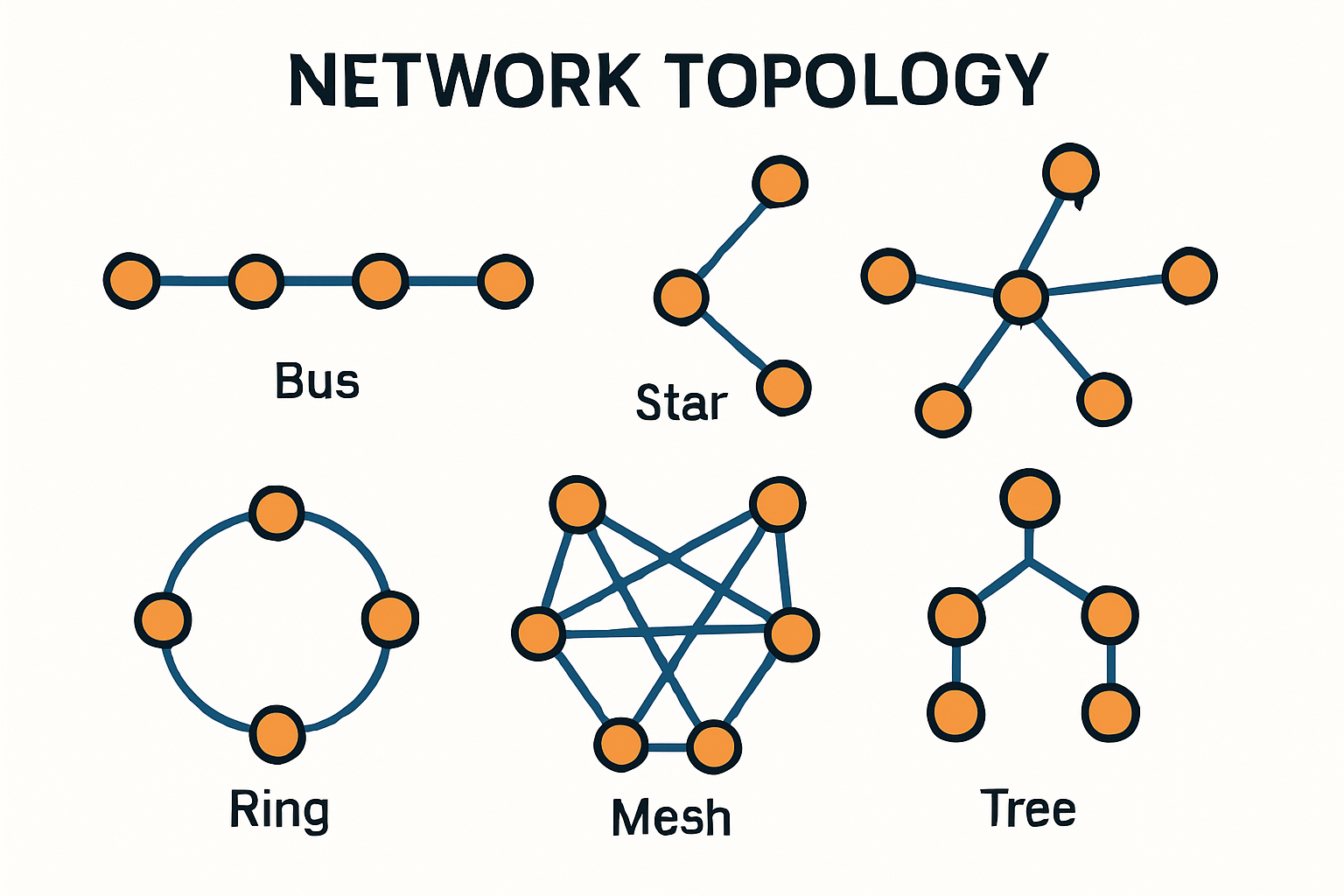
What is a network topology?
What is a network topology? A network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of various elements within a computer network. It defines how[…]
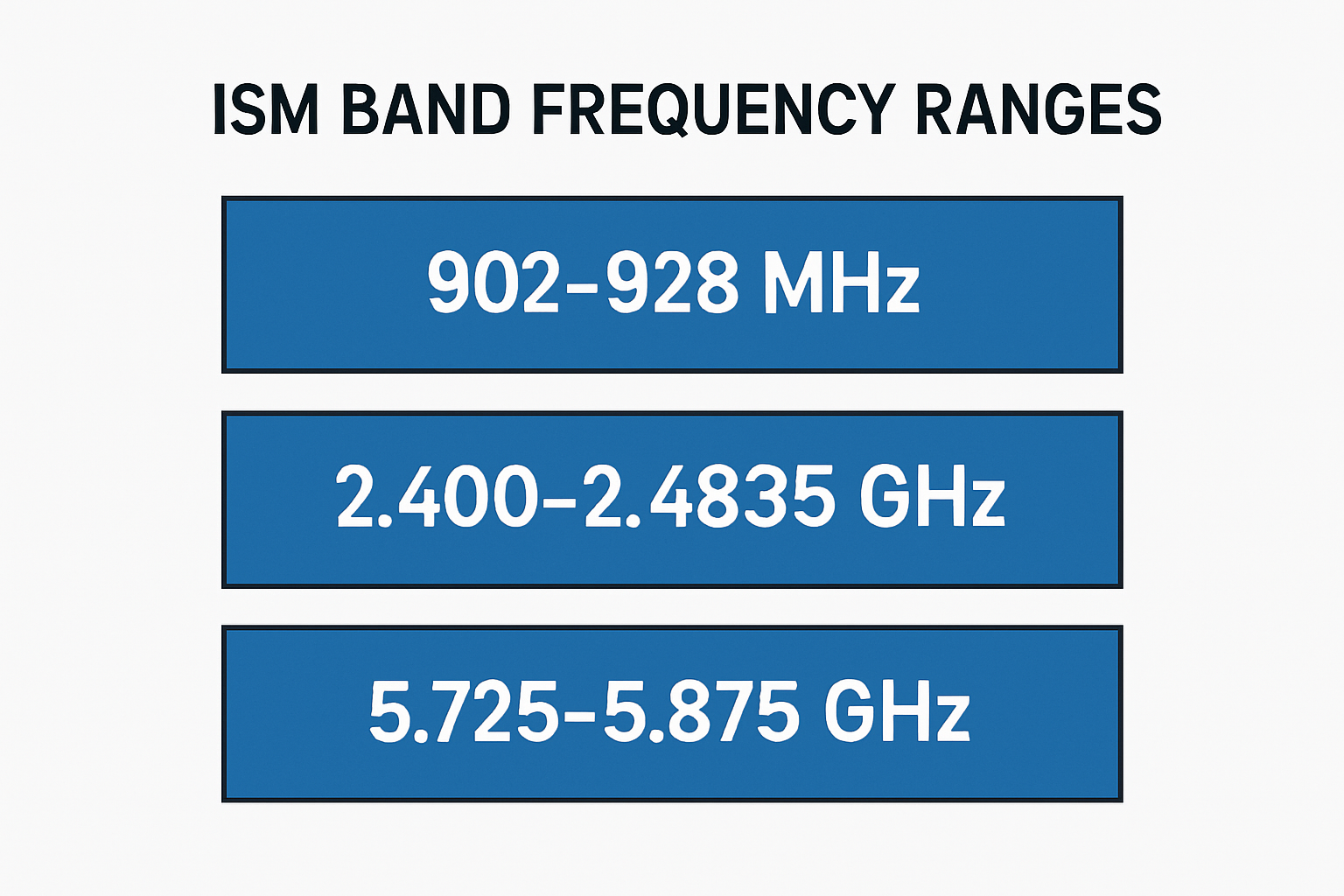
How many ranges does the ISM band have?
The Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) band is divided into several frequency ranges that are designated for unlicensed use across various applications. These ranges are[…]
Discover how Wi-Fi technology revolutionizes connectivity with seamless wireless access, enhancing mobility, flexibility, and convenience in everyday life.
Benefits of Wi-Fi Technology Wi-Fi technology enables wireless connectivity, allowing devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and smart home appliances to communicate with each other[…]

What are routers?
Understanding Routers: Key Devices for Modern Data Communication Routers are essential devices in modern networking that facilitate the transfer of data packets between different computer[…]
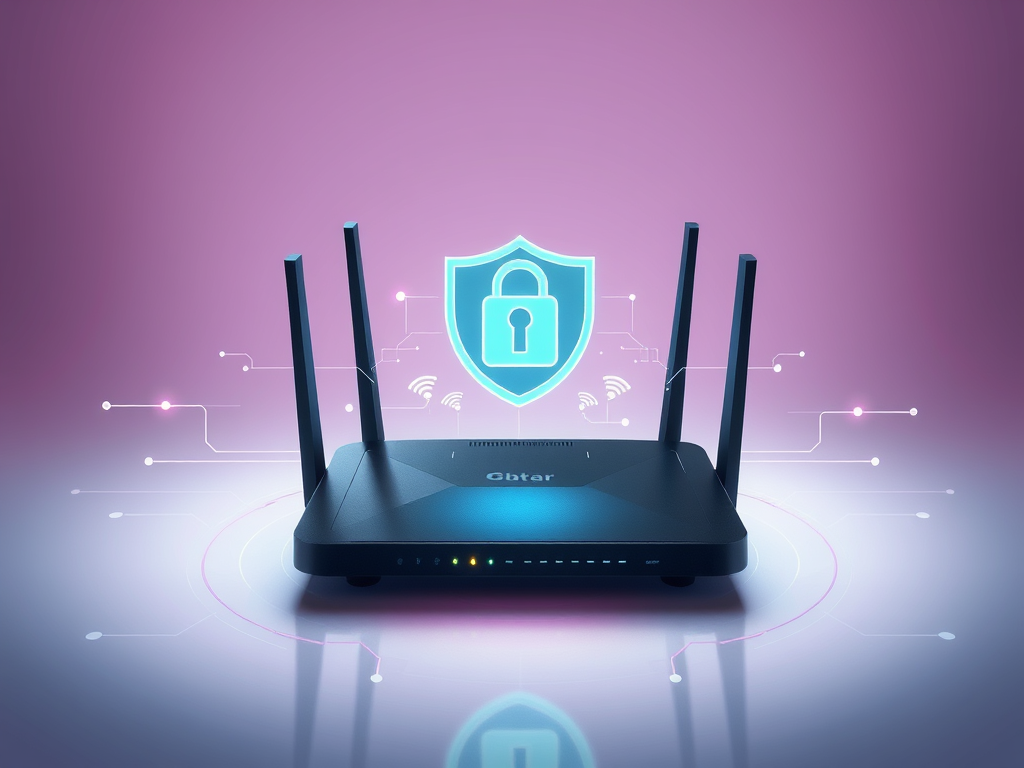

How to Strengthen Your Home Wi-Fi Security
To secure your home Wi-Fi network, change default admin credentials, enable WPA3 encryption, create a guest network, disable WPS, and rename your SSID. Regularly update[…]
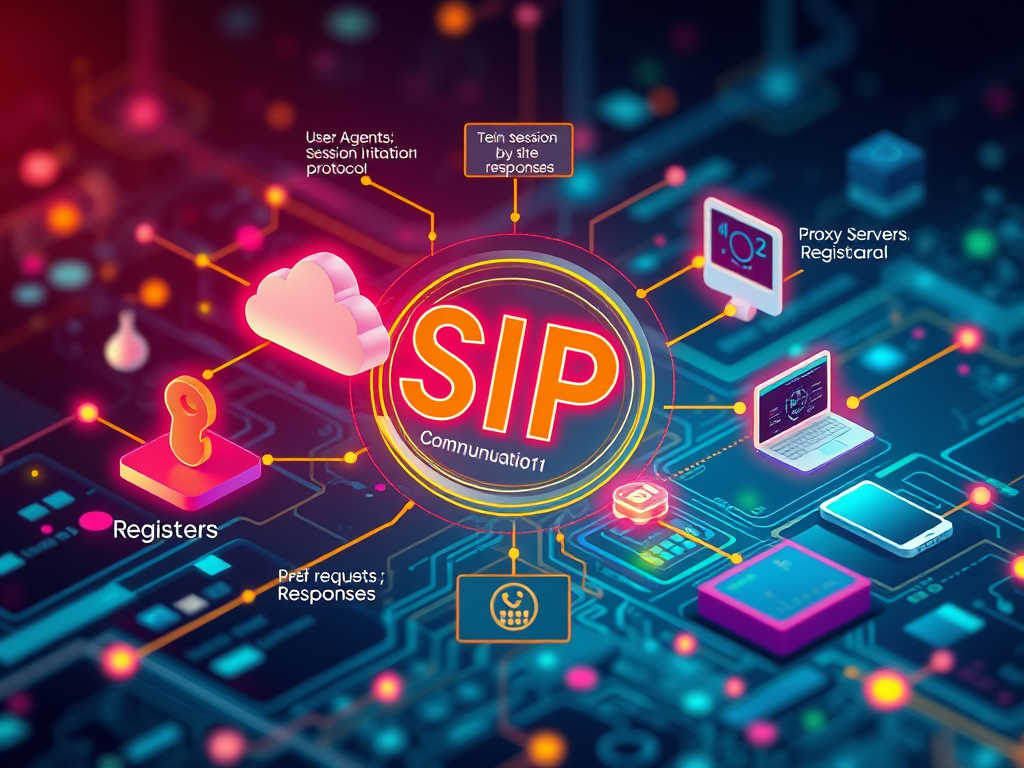
Understanding SIP: Key Components for Real-Time Communication
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is essential for real-time communication, managing sessions in voice and video calls. Key components include User Agents (initiating and responding[…]

Understanding WiMAX Throughput Rates
WiMAX throughput varies based on network configuration, frequency, and users. Fixed WiMAX can achieve up to 70 Mbps under ideal conditions, while Mobile WiMAX typically[…]

Benefits of Wi-Fi in Low-Density Areas
Wi-Fi in low-density areas offers enhanced connectivity and cost-effective solutions for internet access, benefiting residents and businesses alike. It promotes economic growth, improves education opportunities,[…]

Understanding WPA: TKIP vs AES/CCMP Security
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) personal mode primarily uses the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) for encrypting data. However, it is important to note that WPA[…]

The maximum length of an Ethernet cable?
The maximum length of an Ethernet cable depends on the type of cable and the network specifications. For standard twisted-pair Ethernet cables, such as Cat5e[…]

Understanding OFDM and MIMO in Wireless Communication
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is a digital modulation technique that improves data transmission over various channels by splitting streams into sub-streams sent over different[…]

The Birth of Wi-Fi: A 1997 Milestone in Wireless Networking
Wi-Fi was created in 1997 when the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) established the 802.11 standards for wireless networking, which laid the foundation[…]
Key Requirements for a Successful MVP
An effective Minimum Viable Product (MVP) requires core functionality focused on solving user problems, user-centric design for ease of use, a feedback mechanism for insights,[…]

Signs Your Computer Needs an Upgrade
Signs that your computer may require an upgrade include slow performance, frequent crashes, software incompatibility, insufficient RAM, outdated hardware, overheating, limited storage space, graphical issues,[…]

Benefits of Multi-Language IT Support
Having multi-language IT support can be beneficial depending on your organization’s needs. Here are a few reasons to consider: Evaluating the demographics of your users[…]