Network Classification: Understanding Connections and Functions
Understanding key approaches to classify networks
Understanding the TCP/IP Model: Four Key Layers Explained
Exploring the four layers that power internet communication

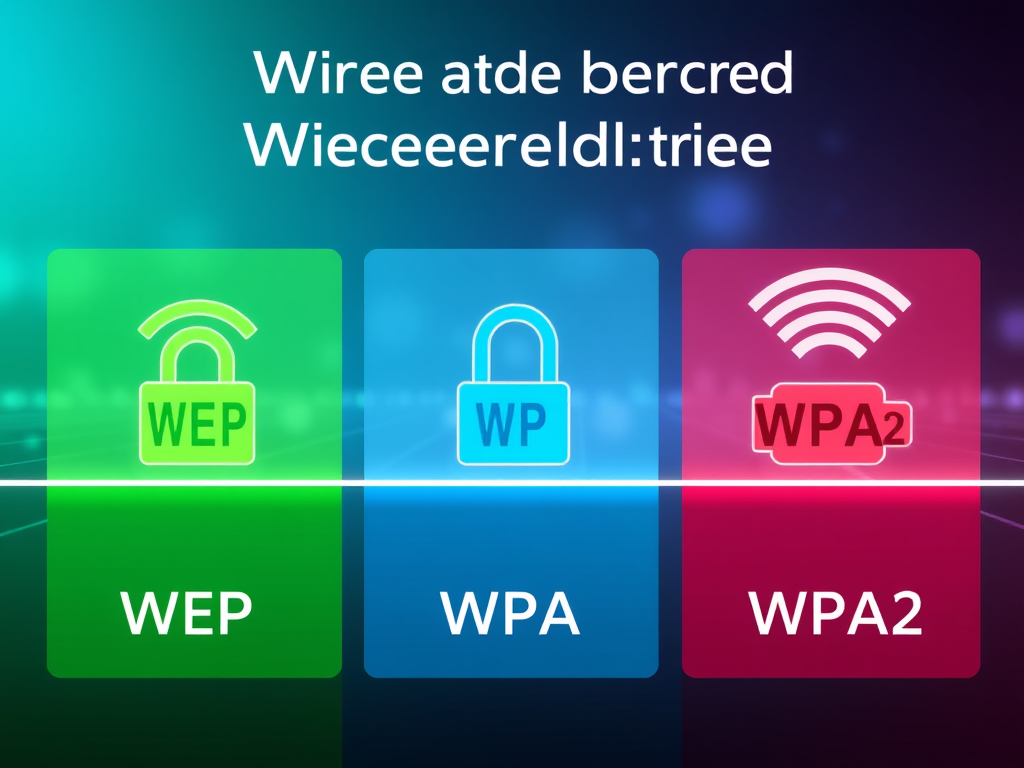
Is Free Public Wi-Fi Safe? Uncovering Risks and Protection
How safe is your data on free public Wi-Fi today?

Maximizing Wi-Fi Range for Better Connectivity
Exploring how Wi-Fi range affects real-life connection
Essential Metrics for Server Uptime Monitoring
Essential metrics and tools for reliable server security

Unlocking Business Growth Through Strategic Service Integration
How real stories reveal the true impact of great service

Understanding Error and Flow Control in Digital Communication
Exploring how network layers ensure reliable data flow
IEEE 802.11g Modulation Explained: Benefits of OFDM
Exploring how IEEE 802.11g uses OFDM for faster Wi-Fi

Benefits of Wireless Networks Explained
A wireless network is a type of computer network that uses wireless data connections for connecting devices. Unlike wired networks, which rely on physical cables[…]

Understanding Rust: A Modern Programming Language
Rust is a modern programming language focusing on performance and safety, ideal for systems programming. Its key features include memory safety through an ownership model,[…]

Mastering R for Data Analysis and Visualization
R is a powerful and open-source programming language for statistical computing and data analysis, offering rich visualization tools like ggplot2. Its diverse applications, demonstrated through[…]

Understanding IEEE 802.11a: Key Features & Benefits
The IEEE 802.11a standard is pivotal in wireless networking due to its high throughput of 54 Mbps and operation in the less congested 5 GHz[…]

Getting Started with React JS: Key Features Explained
React JS is a JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building user interfaces, emphasizing a component-based architecture for improved reusability. Key features include a Virtual[…]

Understanding SHF Transmission: Benefits and Applications
Super High Frequency (SHF) transmission ranges from 3 GHz to 30 GHz, enabling high data rates, shorter wavelengths, and resistance to interference, making it ideal[…]

Understanding TCP/IP: The Backbone of Modern Networking
TCP/IP is a critical suite of protocols that enables data transmission over networks, including the Internet. It comprises TCP for reliable data delivery and IP[…]

Overcoming Common WiFi Limitations
WiFi signals have a range of about 150 feet indoors and are affected by physical barriers. Interference from devices is common, leading to the use[…]

The Impact of IEEE 802.11b on Wireless Networking
IEEE 802.11b is one of the original standards for wireless networking, established in 1999. This standard significantly advanced wireless technology in various sectors, leading to[…]

Understanding Network Cables: A Comprehensive Guide
Network cables are vital for data transmission between devices in computer networks, using copper or fiber-optic materials. They encode data into electrical signals or light,[…]

Understanding Semidefinite Programming: Key Concepts and Benefits
The standard form of Semidefinite Programming (SDP) is expressed as: Minimize: [ C \cdot X ] Subject to: [ A_i \cdot X = b_i, \quad[…]