Understanding the Range and Power of the 802.11g WiFi Standard
The 802.11g WiFi standard, although introduced in the early 2000s, remains one of the cornerstones of wireless connectivity for small businesses, homes, and legacy systems. Understanding its range, power, and performance is crucial for optimizing your network—especially if you operate in environments with mixed devices or signal interferences. Let’s explore its true potential, limitations, and the technical nuances that drive its performance.
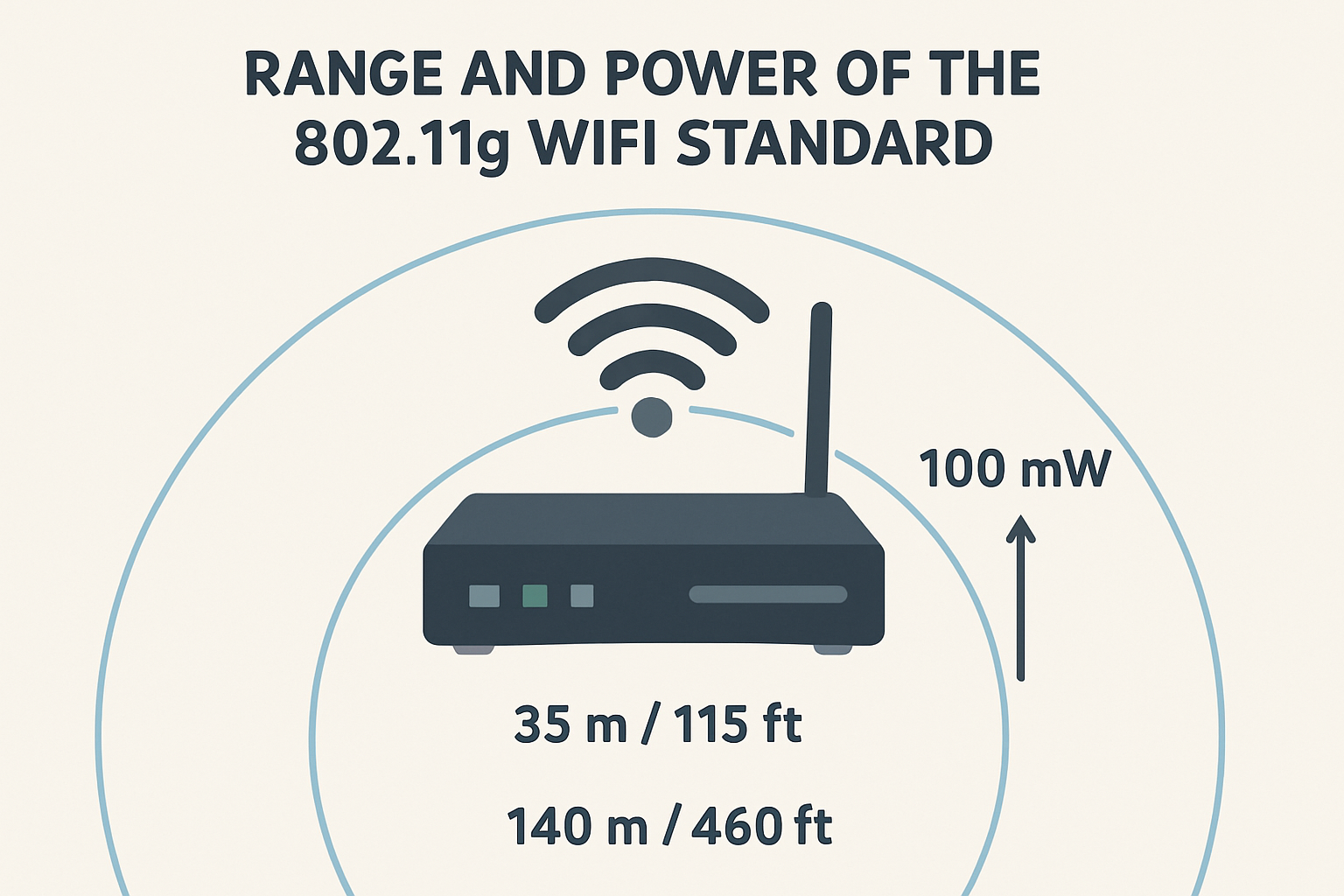
Exploring the True Range of the 802.11g WiFi Standard
802.11g operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, offering maximum theoretical data speeds of 54 Mbps. Under ideal conditions, indoor range typically spans 125 feet (around 38 meters), while outdoor coverage can reach up to 460 feet (approximately 140 meters). However, these figures depend heavily on environmental interference, construction materials, and router positioning. Concrete walls, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth devices can significantly degrade signal strength.
In real-world usage, you can expect effective indoor connectivity in a mid-sized office or household without noticeable speed drops, provided the router is placed strategically. Line-of-sight visibility between the device and router plays an essential role here. Even slight positioning changes—like elevating the router—can improve overall coverage.
Key takeaways:
- Operates on 2.4 GHz frequency, prone to interference but great for distance.
- Offers 54 Mbps under optimal conditions.
- Practical range: 38 meters indoors, 140 meters outdoors.
For a deeper understanding of wireless technology principles, refer to educational sources like How WiFi Works by HowStuffWorks.
Understanding Signal Power and Performance Factors
The power of your 802.11g network depends on both router transmission power (typically 15–20 dBm) and environmental influences. Factors such as overlapping channels, connected device count, and background noise can all impact your WiFi’s stability and throughput. Selecting non-congested channels (like channel 1, 6, or 11) significantly reduces interference in busy networks.
Performance can also vary depending on the connected devices. Newer smartphones and laptops benefit from optimized WiFi antennas and firmware, but older hardware may experience signal degradation. Using WiFi analyzers to measure signal strength helps pinpoint weak spots and optimize router placement.
Pros of 802.11g:
- Cost-effective for small businesses and home setups.
- Great backward compatibility with 802.11b devices.
- Reliable coverage for standard browsing, email, and light streaming.
Cons of 802.11g:
- Limited bandwidth compared to modern standards (e.g., 802.11ac, 802.11ax).
- Interference from household devices.
- Not ideal for heavy data transfer or 4K streaming.
For further insights, check Wi-Fi Alliance’s official documentation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with 802.11g Networks
Even with stable setups, users may face signal dropouts or plugin compatibility issues, particularly when using older operating systems or devices. Common fixes include updating router firmware, checking driver compatibility, and ensuring consistent channel assignment. Sometimes, WiFi extensions or add-ons on network interfaces can create conflicts—disabling these temporarily can help isolate issues.
If your network uses mixed-mode configuration (supporting multiple WiFi standards), 802.11g devices might slow down newer connections. Consider upgrading to a dual-band router to separate traffic and maintain efficiency.
For users who rely on web hosting or IT systems, professional assistance can resolve persistent network interruptions. Archer IT Solutions offers managed IT support, onsite consultations, and remote diagnostics to optimize your connectivity experience. For support, you can reach them at support@archer-its.com or submit a ticket via https://www.archer-its.com/ticket.
The 802.11g WiFi standard serves as a reliable foundation for legacy wireless networks, offering a fine balance of range, speed, and affordability. While it may not compete with modern WiFi 6 or emerging technologies, it remains effective for small operations, classic setups, and users prioritizing stability over speed.
Take a moment to assess your own wireless environment. Do you need better range, faster speeds, or expert management support? Archer IT Solutions can help bridge the gap between your current system and the performance your business deserves.
For more educational resources, check:
Empower your connectivity journey—contact Archer IT Solutions today and bring reliability back to your wireless network.
Discover more from Archer IT Solutons
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
No responses yet