Why Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) is Essential for Modern Connectivity
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) enhances wireless connectivity with a range of about 70 meters indoors and 250 meters outdoors. Its benefits include data rates up to[…]
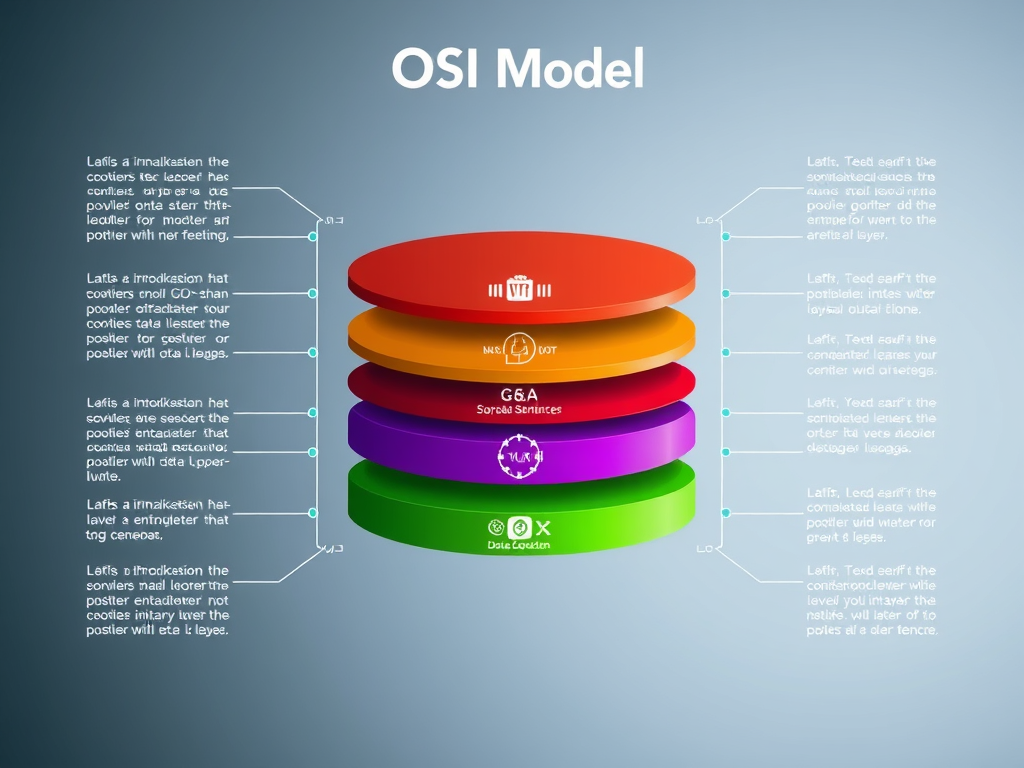
Understanding the OSI Model: Network Layers Explained
The OSI model is a framework guiding network communication through seven essential layers, each with distinct functions. It facilitates data transmission, error management, and user[…]

Exploring Wireless Station Services: A Comprehensive Overview
Wireless station services facilitate wireless communication across various sectors, enhancing accessibility and user experiences. Examples include Wi-Fi hotspots in cafes, connectivity in public transport, smart[…]

Types of Network Cables Explained
Network cables are essential for connectivity, with key types including twisted pair (e.g., Cat 5e, Cat 6), coaxial, and fiber optic cables. Each type offers[…]

Maximize Your Wi-Fi Speed: Tips to Overcome Common Issues
Wi-Fi speeds can slow during peak usage due to network congestion from multiple connected devices. Interference from surrounding networks, bandwidth-hogging applications, and poor router placement[…]

Common Causes of Slow Internet Speeds
Slow internet connections stem from various factors such as network congestion during peak hours, outdated equipment, distance from the router, ISP throttling, and interference from[…]

Benefits of Medium-Frequency Transmission Explained
Medium-frequency (MF) transmission, operating between 300 kHz and 3 MHz, is beneficial for sectors like AM radio, maritime, and aviation due to its wide coverage,[…]

Understanding MAC Addresses: Key for Network Management
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier for devices on a network, crucial for identification and security. Businesses utilize MAC addresses for[…]

Understanding 802.11g: Benefits and Case Studies
The 802.11g standard operates at 2.4 GHz, achieving data rates of up to 54 Mbps. Its benefits are illustrated through case studies: a coffee shop[…]

Understanding IEEE 802.11ac: The Future of Wi-Fi 5
The IEEE 802.11ac standard, or Wi-Fi 5, enhances wireless network performance with maximum data rates up to 3.5 Gbps. It offers benefits like higher speeds,[…]

Understanding TypeScript: Key Features Explained
TypeScript is a JavaScript superset introducing static types to enhance code safety and manageability in large applications. Key features include static typing, interfaces, classes, generics,[…]

Maximize User Engagement: The Key Action for Every Website
Discover what truly matters most for site users

Discover Community Benefits: Engage and Grow with Us
To attract users to your network, emphasize a clear value proposition, a user-friendly onboarding process, and community engagement. Highlight exclusive content, regular updates, and feedback[…]

Understanding Wi-Fi Protected Access: A Security Overview
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security protocol enhancing wireless network security, evolving from the vulnerable WEP protocol. With iterations like WPA, WPA2, and WPA3,[…]

Essential Tech Tips for Small Real Estate Firms
To manage technology support effectively for a small real estate company, focus on robust infrastructure, specialized real estate software, a professional online presence, strong data[…]

Understanding Bandwidth: Key to Faster Internet Speeds
Bandwidth is the maximum data transfer rate of an internet connection, measured in bits per second. Higher bandwidth allows for faster download and upload speeds,[…]

Maximizing Speed with IEEE 802.11n Technology
IEEE 802.11n enhances Wi-Fi speed and range through MIMO technology and channel bonding. To maximize performance, ensure devices support MIMO, enable channel bonding, position the[…]

Understanding Computer Networks: Types and Functions
Computer networks facilitate communication and data exchange between devices, categorized into types such as LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN, and SAN. Their primary functions include enabling[…]

Applications and Benefits of VLF Radio Waves
Very Low-Frequency (VLF) transmissions operate between 3 kHz to 30 kHz, allowing long-range communication and deep penetration into water and Earth. They are utilized in[…]

Understanding Signal Amplifiers: Boost Your Signal Strength
A signal amplifier enhances the initial signal’s power, enabling it to travel greater distances and mitigate interference. These devices are widely utilized in applications such[…]

Understanding SSID: The Key to Your Wireless Network
Wi-Fi networks rely on Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) to connect devices. An SSID is a unique name, visible while searching for networks, helping users identify[…]

Kotlin Programming Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Kotlin is a powerful programming language that requires setting up a development environment. It features basic syntax, such as defining variables, data types, control flow,[…]

The Evolution of Wi-Fi Technology Since 1997
Wi-Fi technology has evolved significantly since the 1997 IEEE 802.11 standard, initially enabling 2 Mbps wireless data transfer. Key developments include 802.11b (1999) at 11[…]

